Wei-Chun WANG, MD
Core Member
Attending Physician, Division of Stroke and Neurocritical Care, Department of Neurology, China Medical University Hospital
Deputy Director, Artificial Intelligence Center, China Medical University Hospital
Education:
MD, College of Medicine, China Medical University
Research Expertise:
Medical artificial intelligence (medical imaging, biomedical signals), Explainable artificial intelligence, Generative artificial intelligence; Neuroimaging, Intraarterial thrombectomy, Neurocritical care
TEL : 04-22052121 ext.12533
醫師 | 王韋竣
核心成員
中國醫藥大學附設醫院 神經部腦中風暨神經重症科 主治醫師
中國醫藥大學附設醫院 人工智慧中心 副主任
學歷:
中國醫藥大學 醫學系 醫學士
研究方向及專長:
醫療人工智慧(醫學影像、生醫訊號)、可解釋性人工智慧、生成式人工智慧;神經醫學影像、急性動脈取栓術、神經重症照護
聯絡電話: 04-22052121 ext.12533
Artificial Intelligence of Stroke Image Analysis
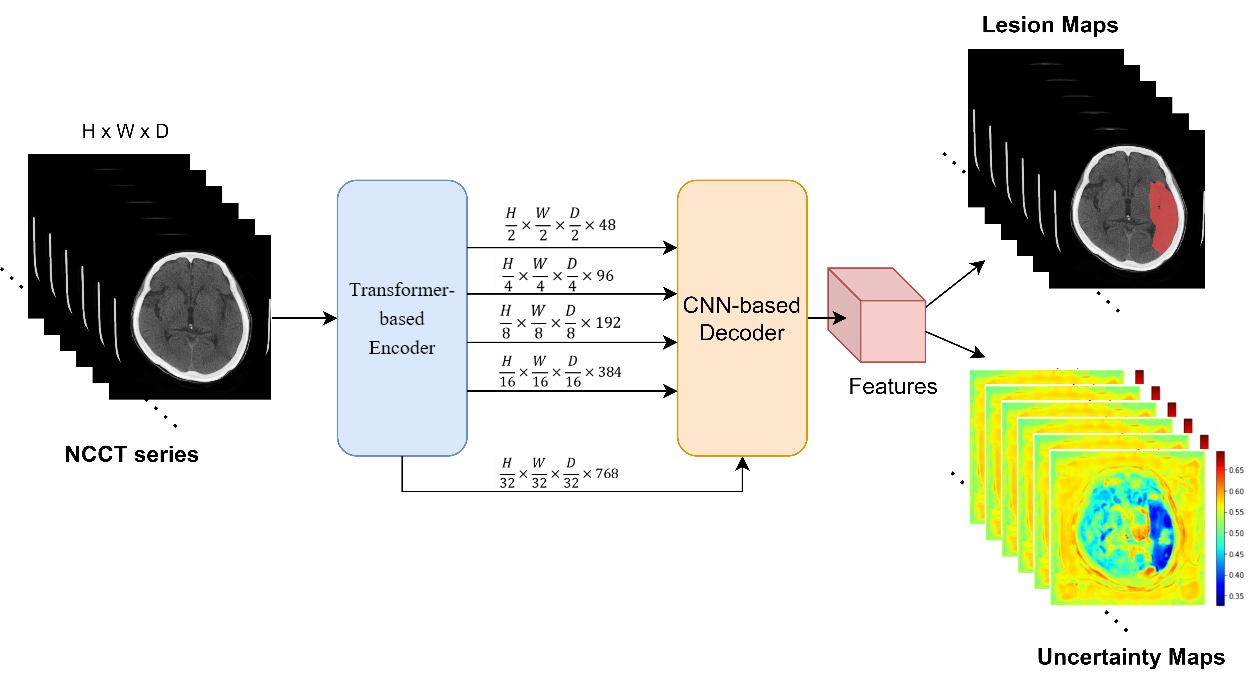
Acute ischemic stroke significantly impacts patients' physiological functions and can be potentially fatal. A breakthrough in AIS diagnosis has been achieved through the development of an AI model utilizing non-contrast CT scans. This innovative approach can quickly diagnose large vessel occlusion in about 30 seconds without contrast injection. The model, based on SwinUNETR architecture, was trained using 317 patient scans from CMUH. Testing revealed a mean Dice score of 46.7%, with a Pearson correlation of 83.46% between predicted and actual lesion volumes. This advancement can benefit hospitals without CT perfusion and help the decision of transfer to larger medical facilities.
Explainable AI in Stroke Outcome Prediction
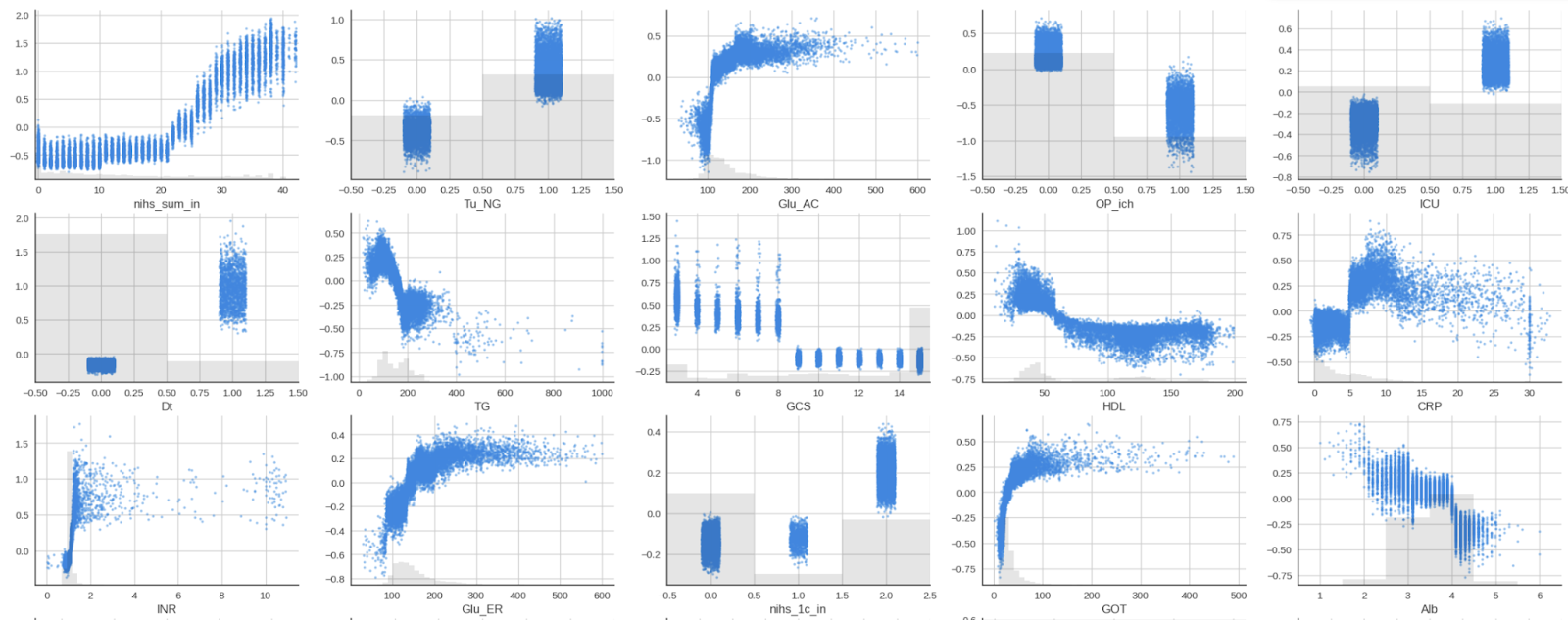
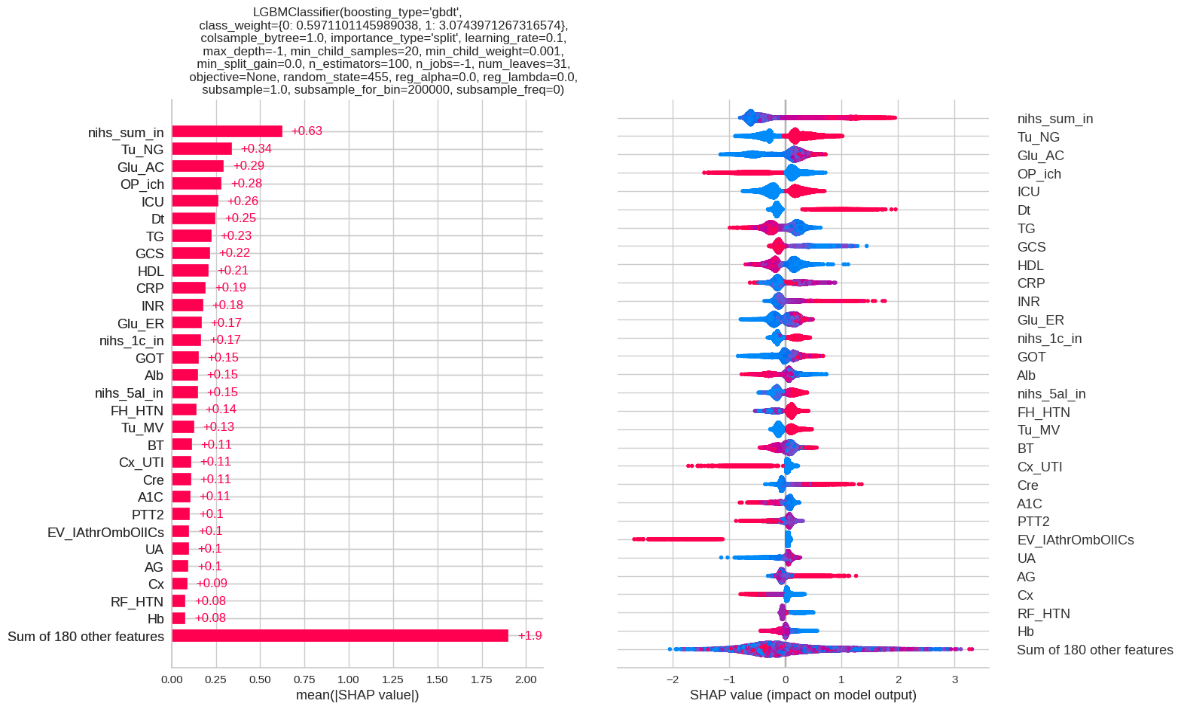
In the study of outcome prediction of acute ischemic stroke, we developed a machine learning model to predict 90-day mortality risk. The SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations), a commonly used explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) technique, revealed several key predictors. The initial NIHSS score (nihs_sum_in) emerged as the strongest predictor, showing a clear positive correlation with mortality risk. Other significant factors included blood glucose levels (Glu_AC), ICU admission status (ICU), and using of nasogastric tube (Tu_NG). Notably, the visualization demonstrates how each feature contributes either positively (red) or negatively (blue) to the model's predictions. This XAI approach provides clinicians with transparent insights into the model's decision-making process, potentially enhancing their confidence in AI-assisted clinical decisions for stroke patients.
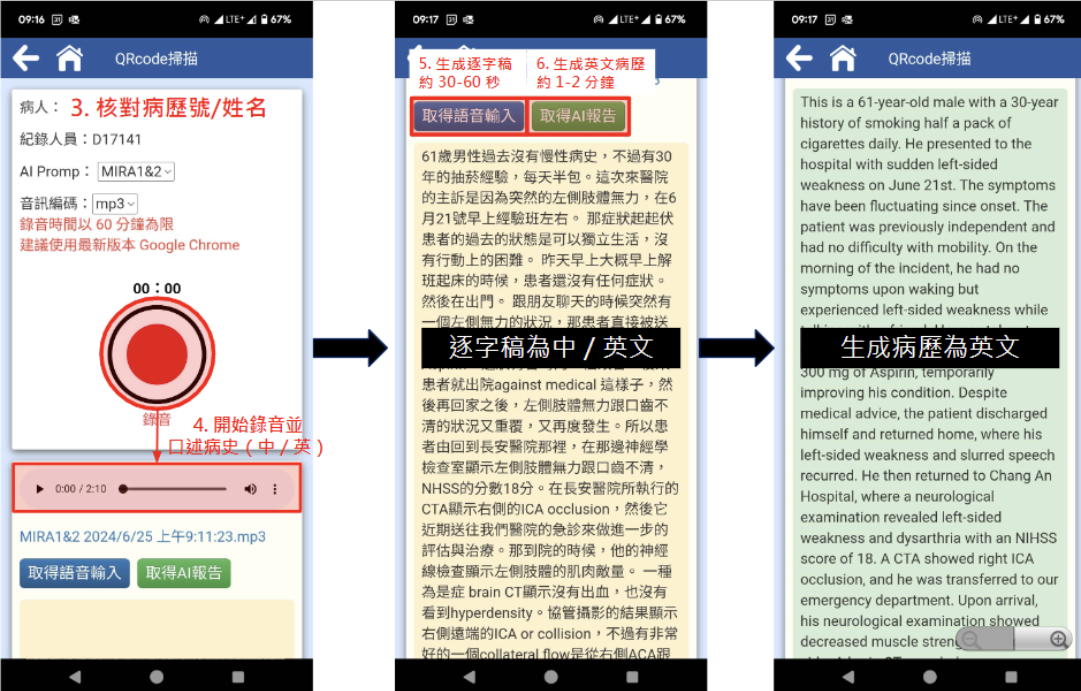
Generative AI in Healthcare
We have pursued its application in healthcare to alleviate the burden on medical professionals through our Multimodal Advanced Generative Intelligence (MAGI) platform. MAGI serves as an AI playground that utilizes a no-code environment, integrating cutting-edge Natural Language Processing technologies, including Large Language Models and Automatic Speech Recognition. This platform transforms healthcare professionals from users into developers, enabling them to develop various applications. Our platform has successfully developed numerous applications, such as an intelligent nursing documentation system that allows nurses to create nursing records through voice input, reducing documentation workload by 75%. We are actively expanding the applications to include automated shift handover note generation, medical record composition, clinical documentation review, and medical education material generation. We aim to streamline clinical workflows and enhance healthcare delivery efficiency.